REQUIREMENTS: Modem, Hub, Repeater and Router
Study Of Network Devices
- Modem:
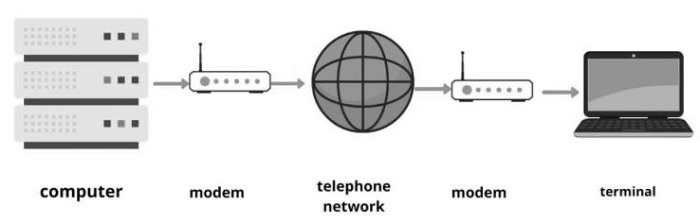
Modem stands for Modulator and Demodulator. It is a device that modulates signals to encode digital information for transmission and demodulates signals to decode the transmitted information.
A modem transmits data in bits per second (bps).
It is necessary for communication between digital devices and Analog devices.
Modem is necessary because it acts as a translator between the devices and rapidly transmits the information.
It converts the digital signal to Analog and vice versa to communicate between devices.
It encodes the signal and decodes at the other end and vice versa between the devices.
There are two types of Modem
Internal Modem: A modem that plugs into an expansion slot within the computer. Unlike an external modem, an internal modem does not provide a series of display lights that inform the user of the changing modem states. The user must rely entirely on the communications program. Contrast with external modem.
External Modem: The external modem is an external part of the computer. It can be used when a computer is unable to fit an internal modem inside of it. The modem typically connects to the computer via a serial or USB cable, and it also needs an external power supply to operate
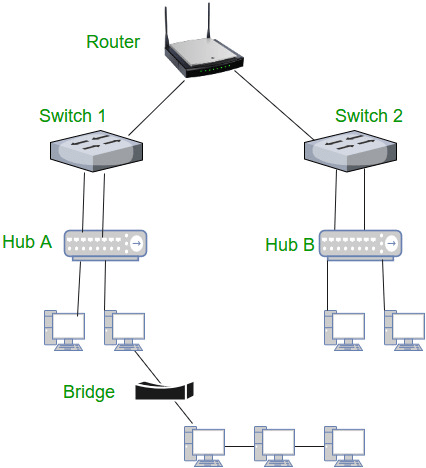
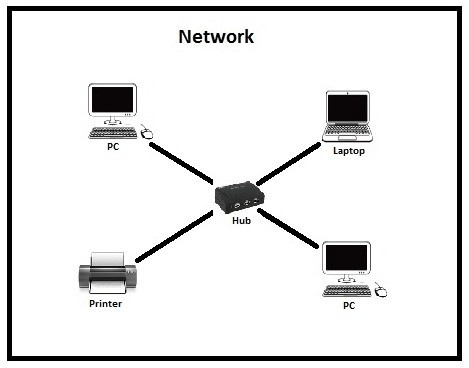
2. HUB:
A hub is a basically multi-port repeater. A hub connects multiple wires coming from different branches, for example, the connector in star topology which connects different stations. Hubs cannot filter data, so data packets are sent to all connected devices. In other words, the collision domain of all hosts connected through Hub remains one. Also, they do not have the intelligence to find out the best path for data packets which leads to inefficiencies and wastage.
Types of HUBS
- Active Hub:- These are the hubs that have their power supply and can clean, boost, and relay the signal along with the network. It serves both as a repeater as well as a wiring center. These are used to extend the maximum distance between nodes.
- Passive Hub:- These are the hubs that collect wiring from nodes and power supply from the active hub. These hubs relay signals onto the network without cleaning and boosting them and can’t be used to extend the distance between nodes.
- Intelligent Hub:- It works like an active hub and includes remote management capabilities. They also provide flexible data rates to network devices. It also enables an administrator to monitor the traffic passing through the hub and to configure each port in the hub.
Repeater – A repeater operates at the physical layer. Its job is to regenerate the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same network. An important point to be noted about repeaters is that they do not amplify the signal. When the signal becomes weak, they copy it bit by bit and regenerate it at its star topology connectors connecting if original strength. It is a 2-port device

Routers – A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses. The router is mainly a Network Layer device. Routers normally connect LANs and WANs and have a dynamically updating routing table based on which they make decisions on routing the data packets. The router divides the broadcast domains of hosts connected through it.